Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines And Angles
LINE
Lines are the straight figures, made up of infinite points, extending infinitely in both the directions. They have negligible depth or width. There are four types of lines: horizontal line, vertical line, perpendicular, and parallel lines.
Note: When the lines or line segments intersect, then angles are formed.
ANGLE
- An angle is a figure formed from the two rays emerging from a common endpoint.
Types of angles:
- Acute angle- Angles less than 90
- Obtuse angle- angles more than 90 but less than 180
- Right angle- Angles equal to 90
- Straight angle- Angles equal to 180
- Reflex angle
- Complementary angle
- Supplementary angle
Vertically opposite angles
When two lines intersect each other, then the opposite angles are called vertically opposite angles. A pair of vertically opposite angles are always equal to each other.
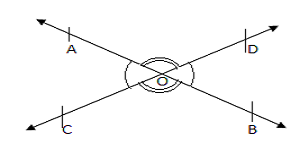
When two lines intersect each other, then the opposite angles, formed due to intersection are called vertical angles or vertically opposite angles. A pair of vertically opposite angles are always equal to each other.
Corresponding angles

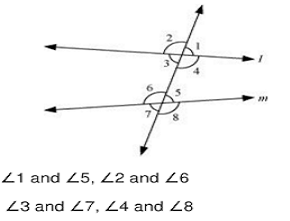
Converse of Corresponding angles

therefor, the line / m are parallel to each other.
Alternate angles
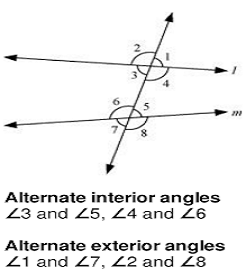
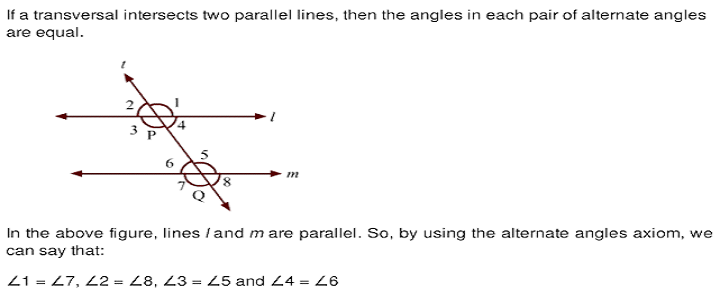
Converse of Alternate angles
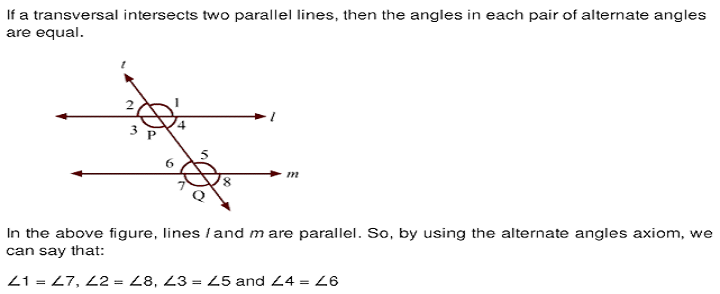
Angle on the same side of transversal

NOTE: The converse is also true.
ANGLE SUM PROPERTY OF A TRIANGLE
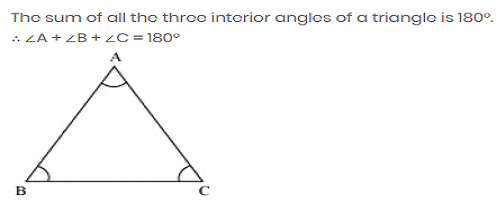

Important note:

Exterior angle theorem
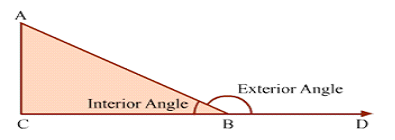

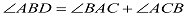
This property is called exterior angle property of a triangle.
Example:
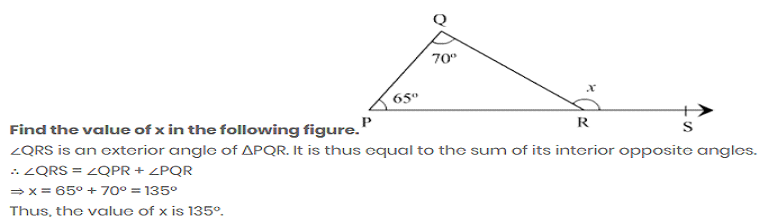
NOTE: